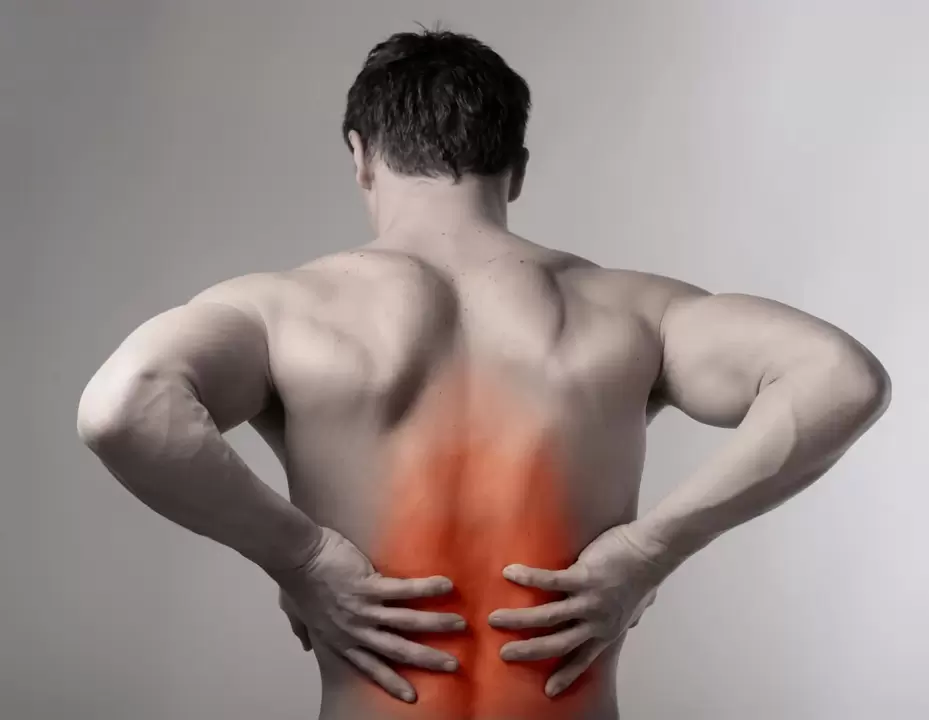
Osteochondrosis is a disease based on degenerative-dystrophic changes that occur on the intervertebral discs, vertebrae and small joints of the spine. Osteochondrosis is a faithful companion of the elderly. However, young people are diagnosed more often, which is probably due to predominantly sedentary work, an unhealthy lifestyle and little physical activity. We can safely assume that the majority of the adult population has signs of osteochondrosis.
Reasons
The elasticity of the spinal column, its mobility and ability to withstand physical activity primarily depend on the condition of the intervertebral discs. The pathological process in osteochondrosis is based on malnutrition of the structures of the spinal column, especially the intervertebral disc. This leads to changes in the normal tissue structure, the intervertebral disc loses its elasticity, its shape changes. Such metamorphoses lead to narrowing of intervertebral discs and, as a result, compression of nerve roots. In fact, these changes explain the appearance of neurological symptoms, especially back pain in osteochondrosis.
In the future, degenerative processes occur in the small joints of the spine, bone growths are formed on the surface of the vertebrae. All these changes lead to a decrease in the flexibility of the spinal column.
Similar transformations of cartilaginous and bone tissue are the result of physiological aging of the organism. But under the influence of certain unfavorable factors, dystrophic changes in the intervertebral joints occur prematurely.These factors include:
- obesity;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Hard physical work;
- Professions characterized by prolonged standing or sitting during working hours;
- Flat feet, valgus foot deformity;
- Deformities of the spine;
- Autoimmune connective tissue diseases;
- Fluctuations in the hormonal background (pregnancy, menopause);
- To play a great sport;
- stress;
- Spinal injuries etc.
Types of osteochondrosis
The characteristics of the clinical picture of the disease depend on which segment of the spinal column the pathological process originated in.There are the following types of osteochondrosis:
- Cervical;
- Thoracic;
- Lumbar.
Cervical osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical region is common. The muscular skeleton of the neck is rather poorly developed, therefore, against the background of osteochondrosis, even with a slight load, the vertebrae are displaced and as a result, the vessels and nerves of the neck are compressed. This explains the specifics of the clinical picture of osteochondrosis of the cervical region.
So, the main signs of cervical osteochondrosis include:
- Constant pain in the neck and occipital region, aggravated by movements in the neck;
- Pain of the hemicranial type - in one hemisphere;
- dizziness, tinnitus;
- Pain in hands;
- A feeling of numbness and tingling in the hands.
Thoracic osteochondrosis
Defeat of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is quite rare. The main prerequisite for the development of the disease is the presence of spinal deformity.
Signs of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- Dull, aching pain in the chest, which is often of a lumbar nature;
- Increased pain when turning the body, sneezing, coughing, laughing;
- Visceral pain in the area of the heart, right hypochondrium, abdomen;
- Numbness, paresthesias on the chest skin.
Lumbar osteochondrosis
The most common variant of osteochondrosis. This is probably due to the fact that the greatest load falls directly on the lumbar region.Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis:
- Painful, less often acute pain in the lower back, which increases with movement or prolonged exposure to one static position;
- A feeling of stiffness in the lower back;
- To reduce pain, a person takes a forced position;
- Aching or sharp pains (like lumbago) in the buttocks, thighs, lower legs;
- Tingling, paresthesias in the legs.
%20with%20lumbar%20osteochondrosis.webp)
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
Radiation methods are used to detect osteochondrosis: radiography, computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the spine. The most characteristic and, most importantly, early sign of osteochondrosis is a decrease in the height of the intervertebral space.
In the later stages of the degenerative process, marginal growths (osteophytes) appear on the surface of the vertebrae. They are easier to detect on lateral X-rays because osteophytes are located in front of and behind the vertebrae.
In addition, in osteochondrosis, the bodies of adjacent vertebrae move, which can also be determined on an X-ray.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Treatment of osteochondrosis is more effective the earlier it starts. As already mentioned, osteochondrosis is a change in the structure of intervertebral discs, vertebrae. Unfortunately, many people ignore back pain for a long time and do not go to the doctor in time, missing the moment when it is still possible to stop the pathological process.
Treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out with the help of medicines, physiotherapy exercises, massage, surgery.
Medical therapy:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets, ointments, injections for pain relief;
- Muscle relaxants;
- Chondroprotectors - promote the regeneration of the affected cartilage;
- Vitamin and mineral complexes;
- Vasodilator drugs;
- Medicines that normalize tissue metabolism.
After eliminating the aggravation of the disease, you should continue with rehabilitation. Therefore, physical therapy is a very important aspect of the fight against osteochondrosis. Performing certain exercises contributes to the formation of a muscular corset. This is extremely important, because thanks to the strong muscular corset, the physical load is evenly distributed along the spine. By regularly performing a set of exercises, the stiffness in the spine will disappear, and the range of motion will increase. Massage, physiotherapy, reflexology and spinal traction will help enhance the effect of physiotherapy exercises.
When complications appear in the form of intervertebral hernia, sciatica, and if conservative treatment fails, surgical intervention is resorted to. The goal of surgical treatment is to remove compression of nerve roots and blood vessels, as well as to stabilize the structure of the intervertebral disc or vertebrae.
Treatment of osteochondrosis at home
Folk remedies will help alleviate the symptoms of osteochondrosis, but in no case will they be able to replace the main treatment. You can find a large number of alternative treatment methods on the Internet, but not all of them are safe, so be sure to consult your doctor.
Traditional medicine

The general principle of folk treatment of osteochondrosis is the use of substances that have an irritating effect. As a result, there is an improvement in blood supply to a certain part of the body, as well as a reduction in pain.
Such a recipe for rubbing is known in folk medicine: mix 0. 25 cups of vodka with 0. 5 cups of honey, add 0. 75 cups of grated radish and two tablespoons of salt. The obtained mixture should be rubbed twice a day on the disturbing area of the back. The procedure must be repeated within a week.
To remove the pain, you can put a potato compress on your back. Grated raw potatoes must be mixed with honey in equal proportions. Then wrap the resulting mixture in cheesecloth, attach it to the back and wrap it with a scarf. You can also use velcro linings. To prepare it, pour one tablespoon of finely chopped burdock leaves into a glass of boiling water. Wrap the mixture in gauze and apply on the back for half an hour. After removing the lining, be sure to wrap your back with a warm scarf.
You can do it even easier: grate a radish, put it in a cotton sock, and then lie on it.
Note:
it is important to be careful when using folk remedies, do not touch your face with your hands. Radish and other herbs, if they come into contact with the eyes, can cause corneal burns.
Physiotherapy
Physical exercises can only be performed outside the period of exacerbation. In case of acute pain, you should refrain from gymnastics, as this will only lead to increased pain.
An example exercise set might look like this:
- Lie on your back and straighten your legs. Pull the foot of the right foot towards you and the toe of the left foot away from you. This must be done in order.
- Lying on your back, place your hands behind the back of your head. The legs must be together and bent at the knees. The knees should be bent to the left side, and the head should be turned in the opposite direction. Hold for just a few seconds. Then move your knees to the right and your head to the left.
- Lie on your back, arms by your body. You need to bend your knees and lift your pelvis. Stay in this position for a few seconds. As you exhale, lower your pelvis.
- Turn to your side. Straighten the top leg and swing it back and forth.
- Starting position on all fours. Arch your back, hold this for just a few seconds, then arch your lower back.
- Roll onto your back. Pull the bent left knee to the right elbow and then vice versa.


























