Arthrosis of the hip joint (coxarttrose)- This is a chronic degenerative joint disease leading to the deformation of bone tissue.With coxartrosis, all components of the joint are included in the pathological procedure: articulated cartilage, bone structures along with cartilage, sinoviška shell, ligaments, capsules and adjacent muscles.In the event of a disease, the articulated cartilage is destroyed, the micro-redimistic bones and osteophytes appear (bone growth) and inflammation of the muscular ligament hip joint.
In the world every fifth person complains about joint joint problems.It can also be pain or restricting movement in the joints and combinations of these symptoms.Any other outpatient vision falls on patients with bone-muscle disorders, while 66% of cases are younger than 65 years old.According to the latest epidemiological research, the prevalence of the arthrosis of the knee joints and the hook among the adult population is 13%.
Risk factors for coxartrosis development:
- Genetic predisposition.The common cause of coxartrosis of hip joints is a congenital or acquired mutation type II Type Type II.
- Staros old age.The probable cause of the prevalence of arthrosis in age is a deviation between harmful influence on the articulated cartilage of the external environment and its renewal capabilities.
- .Women suffer from osteoarthritis more often than men.This is due to the influence of the impact of female sex hormones of estrogen on the metabolism of the bones of mineral metabolism.However, the influence of the floor is ambiguous - according to some authors, unlike damage to other joints, there are no differences in a sexual basis for coxartrosis: in men, the arthrosis of the side joint is often found in women.
- Excess body weight.The relationship is proven between excess body mass and the appearance of arthrosis.The excess adhesive tissue increases the harmful load on the cartilage.In addition, adipose tissue produces pro -inflamatory enzymes that damage the cartilage tissue.
- Frequent development of bones and joints.In accordance with the studies, 80% of coxartrosis, which occurs without obvious reason, is related to the previously non-diagnosed shortcomings in the development of joint hip - dysplasia and subclusion.
- Heavy physical work.Excess loads on hook compounds with certain types of physical work can result in damage to the joints and formation of arthrosis.At risk, agricultural workers, diggers and people of similar work specialties are at risk.
- Injuries.The risk of coxartrosis development increases after the injury to the hip joint.Moreover, one injured wrist and both can be included in the process.
- Professional playing sports.Professional sport can cause coxartrosis and due to excessive load on the joints and due to injuries.Potentially dangerous sports include severe athletics, athletic jump, parachute sport.
- Bones and diseases of the joints- rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, common infections, avascular necrosis, gouty arthritis, etc.
- Endocrine pathology- Hypothyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, acromegaly (damaged front pituitary function), diabetes, obesity.
If similar symptoms are discovered, contact your doctor.Don't self-synchronize - it's dangerous for your health!
Symptoms Arthrosis Hook's joint
The main symptoms of coxartrosis include: pain, mobility and crumbly restrictions in joints, their deformation, functional shortening of lower limbs and periodic swelling in the joints.
Pain of various intensities.The pain in the wrist is initially slight and appears for a short time.They appear or intensified as they walked or with other physical efforts, for example, during squat, tendency and weight lifting.As the disease is developing, the pain is enhanced, and even a long vacation does not make relief.In addition, the pain appears with long-term reality and fixation of the joint in one position.
Patients complain about such-thecalated "initial" hip joints after sleep, car driving and other prolonged reality."Starting" coxartost pain takes no more than 30 minutes.The pain is enhanced during hypothermia or in a stressful situation.They can be localized in the area of buttocks or groin, on the front or side surface of the thigh.With all over the nerves above the nerve of lumbar plexus, it can be transferred to the thighs of the center of the body or in the knee.Sometimes pain relates to the lumboslorn spine and forward.
Limitation of common mobility.Movement in the joint of the hip with coxartrosis are limited due to pain.At the same time, rotation (converts both inside and externally) and bringing the lower limb (movement to the middle of the body) is more often disturbed, but it can be limited (movement from the middle axis of the body), as well as flexion and extension.Inability to make passive joint movements due to the pronounced pain syndrome causes compensatory pelvic bias.Patient walking changes, buttocks stick back, the body deviates forward when transmitting weight on the damaged side.With bilateral damage in patients with coxartrosis, a "duck walk" was formed.
Occasionally occasionally occurring by coxartrosisswelling in the wristwhich can be invisible due to layer of muscle and fat.Also, the disease is characteristicCryst in the joints during the movement, their gradual deformations and functional shortening of the lower limbs.
Often one wrist is affected by the disease, then the procedure applies to others.But sometimes arthritis affects several joints at once, and gifts appears.PolyosteoAAAAAART is characteristic of older people or with hereditary predisposition and simultaneous diseases - diseases of bones, joints and endocrine disorders.
Pathogenesis arthrosis hip joints
In pathogenesis Arthrosis Hook, an important role is played by mechanical impairment (injuries and microtrows due to increased physical efforts) and genetic, hormonal and metabolic factors.It is often not possible to find out which factor influenced the development of disease in a particular patient, but often the disease is developed after the mechanical injury damage.
The tissue damage stimulates the subdivision of crispy tissues (chondrocytes), while production of pro -inflammatory cytokines increases, which are usually present in cartilage in only small quantities.The cytokines launch the inflammatory process, for example, influenced by the PRO-inflammation cytokine IL-1, the enzymes that destroy the cartilage wrist.Also, under the influence of cytokine, production of TSOG-2 enzymes and other substances that have a toxic effect on convulsiveness.
Sonoviti also play a big role in the development of coxartrosis - inflammatory disease of the sinovian husk joints or ligaments with the accumulation of liquid in the cavity.
The reduction of elasticity and strength of articulated cartils associated with metabolic disorders leads to a reduction of its resistance to mechanical stress.With coxartrosis, all components of the compounds are included in the pathological process, including subchongral bone.Due to the fact that the large joints of the lower extremities make up large joints of the body, they experience significant mechanical stress, which is why microallomas occur in a subhondral plate and cartilage.As a result of the microwel, the subchongral bone is compacted, leading to regional growth of bone tissue - osteofit.And that, in return, encourages further degradation of articulated cartilage.
In some cases, the arthrosis of the hip joint is inherited.Hereditary arthrosis is allegedly inheritance polygen - due to the action of many genes, each of which affects weak.The cause of some diseases is a mutation in genes that encode macromolecules of articulated cartilage, which causes its ruptures.The genes responsible for the division of hondrocytes can also suffer.In addition, metabolic disorders are inherited, such as pyrophosphate arthropathy - a disease in which the crystals of pyrophosphate calcium accumulate in articulated cartilage and synovial fluid.
Classification and phases of the development of the Arthrosis of the hip joints
Depending on the causes of the disease, cocsart is divided into two main forms: primary (idiopathic) and secondary (incurred from other diseases).
Primary coextress:
- Localized (Hook's joint only):
- unilateral;
- bilaterally.
- Generalized (polioaaaarthrosis) with a lesion at least three common groups (for example, hips, knees and small joints of brushes or feet).
Secondary arthrosis:
- Post -Traumatic:
- acute - as a result of acute injury;
- Chronically - due to the class of some sports or as a result of professional activity.
- Metabolic diseases (ocoin, hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease, gaucher disease).
- Congenital pathology and development (congenital dysplasia hip joint, PERTES Illness, Cleaning the bone epiphysis, hypermobility syndrome, lower limbs, scoliosis, displasia bones).
- Endocrine pathology (acromegaly, hypothyroidism, diabetes melitus, hyperpariariatorism, obesity).
- Calcium salts (pyrophosphate arthropathy, calcification of tetivnis).
- Bone and joint diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, pedentical disease, avascular necrosis, infection).
According to clinical events, the following forms of coxartrosis are included:
- Small symptomal.
- Manifesto manifests bright clinical symptoms:
- quickly progressive, in which symptoms develop in the first four years since the beginning of the disease;
- Slowly progressively - clinically significant symptoms appear after five years of course of the disease.
In accordance with X -Ray images, two types of hip joint arthrosis can be identified:
- Hypertrophic - with signs of increased reparative response (lesions are replaced by new tissue, for example, osteofiti appear);
- Atrophic (reduction of tissue strength).
The stages of the disease can be determined radiologically and clinically.To determine the radiological phase of the hip joint arthrosis, Kellgren classification and Lawrence (1957) is most often used.
Phases of arthrosis in the radiological classification
| Phase | Signs |
|---|---|
| 0 | There are no signs of arthrosis in x -ray pictures |
| 1 | The joint gap does not change, individual regional osteofits are visualized |
| 2 | The joint gap is not changing, significant regional osteophytes are visualized |
| 3 | The amount of the shared gap is moderately reduced, significant regional osteophytes are visualized |
| 4 | The height of the common gap is significantly reduced, significant regional osteophytes and subhondral osteosclerosis (bone tissue compaction below the lower surface of the cartilage with cartilage structure |
In order to determine the clinical phase of the disease, classification (1961) using both clinical signs and visualization criteria is used.
Clinical phases of arthrosis
| Phase | Signs |
|---|---|
| 0 | The articular gap is undivided and unequal, the edges of the articulated cracks are slightly indicated (initial osteofiti), a slight restriction movement was recorded |
| 1 | The victim's gap is significantly narrowed (50-60%), significant osteophytes, subhondral osteokosclerosis and cystic enlightenment in the bones of epiphyses;The clinic prevailed with the restriction of mobility in joints, rough crumbs during movement, insignificant or moderate muscle atrophy |
| 2 | Deformation, joint rigidity;The articulated gap narrowed by more than 60-70% of norms or completely absent, extensive osteophyte, subhondral cysts, articulated "mice" are visualized bones, cartilage or mixed pathos found in the common cavity |
Complications of the arthrosis of the hip joints
With a coxartrosis, all complications are connected with the pathological changes in the joints.
Coxartrose flow can be complicated with local inflammatory processes:
- Burde - inflammation of synocular bags in the joints;
- tenfovaginitis - inflammation of the internal shell of the vagina muscle tendons;
- Tunnel syndrome-pecke nerves due to the creation of large osteophytes or with articulated deformations.
With the advancement of coxartons and its transition to II and III clinical phases, the pain restricts the mobility of the common, and over time, there is a common anchylosis (fibrous, bone or cartilage), accompanied by complete immovable.
A significant deformation in the joint can lead toFractures or aseptic bone necrosis.For coxartrosis, aseptic necrosis of femur is the loudest complication.
Coxartroses may appearFacial and dislocation of wristas well as penetration of the thigh head in the pelvic cavity.Dislocations and subluxation hip joints lead to pain (in the first acute, then dull and painful), intensification during walking and other physical effort, as well as for the deformation of common, chromium, and sometimes to shorten the affected limb.
Despite the lack of systemic events of arthrosis, in modern clinical practice, more attention is paid to diseases associated with him.These are such pathological conditions that exist or appear on the background of the current disease.In relation to inflammatory reactions that arose during the arthrosis, the formation of atherosclerotic plates on the internal walls of the vessel, which increases the riskCardiovascular diseases.Reducing physical activity due to pain and limitations of common mobility leads toObesity, depression and deterioration in quality of life.With extended use of non-anti -infalmato drugs,The upper gastrointestinal sections are affected,And alsoThe risk of cardiovascular pathology and kidney diseases increases.
Diagnosis of Arthrosis Hook's joints
The diagnosis of "coxartrosis" is performed on the basis of clinical events and radiological examinations.There are no characteristic laboratory characters for arthrosis diagnosis.
Among clinical eventsThe main thing to diagnose arthrosis hip is pain and its character.The pain for the arthrosis hip joint occurs and grows gradually over a few years (sometimes a few months with a fast progressive shape).Pain appears or reinforces during physical effort or in standing position.If the patient begins to feel pain alone, then inflammation (sinovitis) joined.The statement noticed up to 30 minutes in the morning and with prolonged real estate.
The restriction of joint mobility gradually increases, this also applies to active and passive movements.With disease development are deformed compounds, functional limb length can occur.
On the study of physicsThere is a constraint of common mobility, their deformation, limb shortening, pains in the palpation of the wrist and a large spinning bone, muscular atrophy.
Laboratory methodsFor the diagnosis of the hook arthrosis are not required.However, they can be used for a differential diagnosis of coxartrosis with arthritis (rheumatoid and chronic), because there are no inflammatory changes in the total blood test and rheumatoid factor, and the urethric acid levels are not increased.In addition, the use of laboratory tests reveal contraindications for medication methods.
Instrumental methodsTo diagnose arthrosis hip joints:
- Radiography- This is the main method of diagnosing arthritis of hip joints.The radiograph determines changes characteristic of coxartrosis: narrowing of a common jazette, osteophyte, erosion and ulcerations of cartilage, subhondral cysts and osteosclerosis.The X -Ray examination is a classic method for coxartrosis diagnostics, and radiological signs of subdogs are the classification of coxartrosis.However, there are currently more and more use of other methods of wrist visualization, such as ultrasonic and magnetic resonance.
- Ultrasonic examination (ultrasound) -The advantage of ultrasound is in the absence of radial load on the body.
- Magnetic resonance tomography (MRI)- Compared to other methods, it allows you more clearly visualize community damage.
- Arthroscopy-It allows you to identify damage to the articulated cartilage: from hondromatice zones in diameter less than 10 mm to a deep crack that penetrates subhondral bone and form deep rectors.Superant and medium cracks and surface erosion can be visualized.
The identification of coxartrosis does not usually represents special difficulties, but when assessing a certain clinical situation, it is necessary to remember the possible secondary origin of the hip compound (as a complication of other diseases, for example, with endocrine disorders).
Treatment Arthrosis Hook's Joint
Treatment Arthrosis Hooks can also be conservative (medications and non-closed) or operational.Conservative treatment is used in 1-2 phases of diseases, surgical 3 phases.Surgical treatment can be recommended in 2 phases with permanent pain and lack of reaction to conservative therapy.
Objectives of conservative therapy:
- improve the quality of life - reduce pain and increase common mobility;
- Stop or slow down disease development.
Methods of treatment that are not an Idrug include:
- Unloading the hip connection (reduction of body weight, creating additional support and transmission of body weight in a stick or crutch);
- Physical education of physiotherapy;
- Physiotherapy treatment methods.
Cock cartridge treatment begins with methods that are not protruding, the important role is given to the exercises of physiotherapy.With a strong pain, the patient should use support.With pronounced disease and the presence of contraindications to the endopripetet, support must be used for a living.
Cuxartrosis TherapyIncludes medications that reduce the symptoms of the disease.These are analgesics, as well as medications from the group of non-atenenal drugs (NSAIDs).NSAIDs are divided into the non-precection and selective.
Analgesics and NSAIDs for arthrosis hook joints are briefly used to relieve pain and inflammation.There is currently no proven advantage of a non-asterical anti-inflammatory agent over another, so the choice of a particular drug depends on the side effects and a certain clinical situation caused.
It must be borne in mind that NSAIDs have numerous side effects.When you take them, the mucous membranes of the stomach and twelve, as a result of ulcers and bleeding possible.Numerous NSAIDs have toxic effect on liver and kidneys.In addition, NSAIDs interfere with the pairing and, as a result, the patient is disturbed by thrombosis and there is a bleeding tendency.The NSAID with long-lasting use combat the processes of hematopoies and may cause abandon anemia and agranulocytosis.The reception of selective NSAID causes significantly smaller complications.
Special fats and gels used locally cause less side effects from oral products.Medications for heating and reducing pain are used to treat arthrosis.They can contain turpentine, menthol, nicotine acid esters, salicilate, bee poison.Also, NSAIDs have a good effect.
In the absence of an analgesics and NSAID effects or if it is impossible to select the optimal dose of the drug, the hospital of central action can be prescribed.
In case of inflammation, the intra -articular administration of the corticosteroid is used.Corticosteroids are not used no more than 2-3 times a year, because more often use can lead to cartilage degeneration.
Slowly behaving drugs weak symptoms of disease include hondroprotectors, inappropriate areas of avocados or soy, hyaluronic acid.These drugs are included in the recommendations of the European Antirematic League for Treating Arthrosis Hook.Preparations reduce pain and improve common mobility.
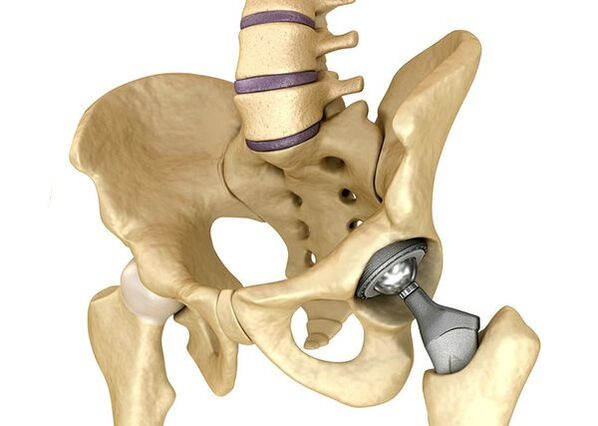
EndoProsthetics of hip jointsIt is used in severe cases of Phase III, when pain syndrome cannot be eliminated, and mobility is common significantly limited.The prosthetics of the hook joint leads to a reduction in pain syndrome, improve the functional state of common and quality of the patient's life.The effect lasts 10-15 years, after which another operation can be sought.During the operation, the wrist of the hips was replaced by artificial imitation of ceramics, metals (most commonly used titanium prostheses) or polymers.
Forecast.Prevention
The forecast arthrosis hip joints in relation to the patient's life is favorable, but the disease often leads to disability.According to the World Health Organization, 80% of older patients with coxartrosis has violation of mobility, and 25% cannot do everyday things.In this regard, the primary prevention of the hip joint arthrosis is important.
Prevention measures:

- Reduce body weight.It is necessary to adapt the nutrition to reduce the weight and load on the compound.In addition, reducing the amount of adipose tissue reduces the amount of inflammation of the mediators who have released.
- Avoid hard physical work and sports overload.Physical overloads are often the cause of the hip joint arthrosis, while moderate physical activity, on the contrary, improves the condition of articulated cartilage, retains its normal mobility and reduces the load on other compounds.
- Correct the basic disease.If the patient is detected in diseases that can lead to secondary coxartrosis (endocrine, rheumatic and other), a basic disease is needed.Normalization of the hormonal background and achieving a persistent remission of rheumatic diseases and is primarily the prevention of arthrosis and allows you to slow down its development.
- Take a healthy lifestyle.Balanced diet with sufficient facilities of plant and animal proteins, polynesy fatty acids and limiting simple carbohydrates, as well as moderate physical activity, avoid the occurrence of coxartrosis even in the presence of risk factors.
Currently, the prevention of the hip joint disease is mandatory in neonatology and pediatricians.Over time, a customized congenital dysplasia blend of hips significantly reduces the risk of coextrose in adulthood.


























